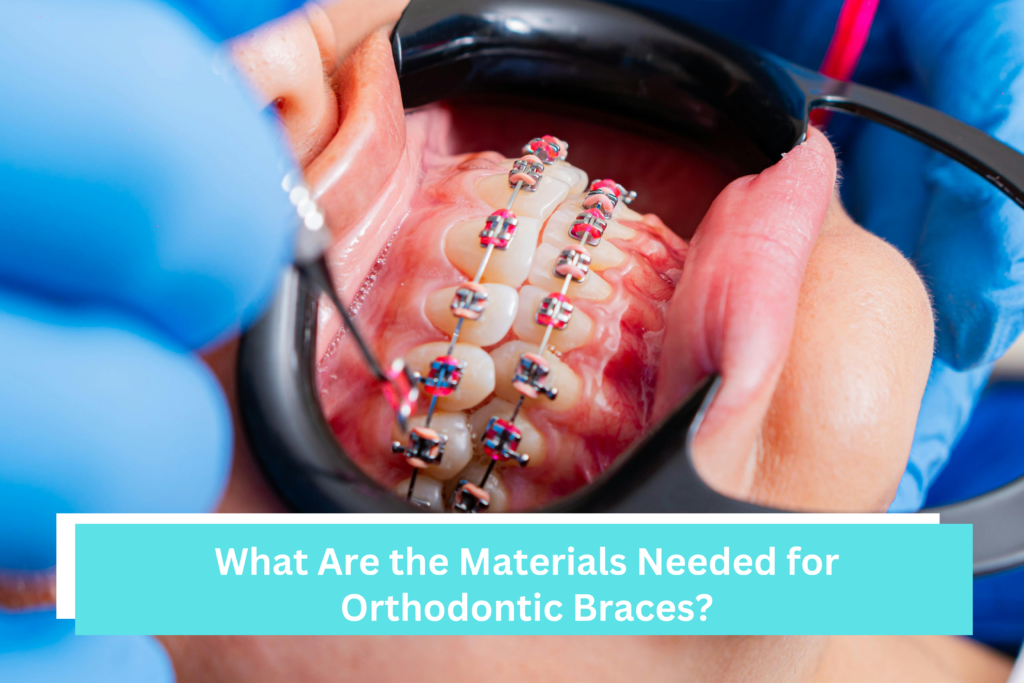
Orthodontic braces consist of several key materials designed to straighten teeth, primarily including metal or ceramic brackets, archwires (stainless steel or nickel-titanium), elastic ligatures, adhesive bonding resin, molar bands, and buccal tubes. These components work together to apply consistent pressure, with optional accessories like wax for comfort.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore all the materials needed for orthodontic braces, their functions, types, and how they contribute to successful teeth alignment.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the Core Components of Orthodontic Braces
Orthodontic braces are not just metal wires on teeth. They are carefully engineered systems made from advanced dental materials designed for durability, safety, and comfort.
Let’s break down each component.
Brackets: The Foundation of Braces
Brackets are small square-shaped attachments bonded directly to the front of each tooth. They act as anchors that hold the archwire in place and control tooth movement.
Types of Brackets
Brackets: Attached directly to the teeth to hold the wire, made from stainless steel, ceramic (clear/tooth-colored), or sometimes plastic.
Common Materials Used for Brackets
- Stainless Steel: Strong, durable, and cost-effective.
- Ceramic (Aluminum Oxide): Tooth-colored for a more aesthetic appearance.
- Plastic (Less common, mostly for temporary use).
- Cobalt-Chromium: High-strength, corrosion-resistant material for specialized brackets.
Stainless steel brackets are the most commonly used due to their reliability and affordability, especially in traditional orthodontic treatments offered in Abu Dhabi dental clinics.
Ceramic brackets are preferred by patients seeking a more discreet option since they blend naturally with tooth color.
Archwires: The Driving Force Behind Tooth Movement
Archwires are thin metal wires that connect all brackets. They apply controlled pressure to guide teeth into their desired position.
Archwires: Metal wires (often nickel-titanium or stainless steel) that connect the brackets and guide teeth movement.
Common Archwire Materials
- Nickel-Titanium (NiTi): Flexible, shape-memory wire used in early stages of treatment.
- Stainless Steel: Stronger and less flexible, used in later stages.
- Cobalt-Chromium: Used for high-strength requirements.
Nickel-Titanium (NiTi) wires are particularly effective because they return to their original shape, applying continuous pressure for gradual tooth alignment.
Ligatures (O-Rings): Holding Everything Together
Ligatures are small elastic bands placed around brackets to hold the archwire securely.
Ligatures (O-rings): Small elastic bands that fasten the archwire to the brackets, available in various colors.
Patients, especially younger ones, often enjoy choosing colorful ligatures to personalize their braces. Orthodontists in Abu Dhabi frequently offer a wide color selection for customization.
Bonding Adhesive: Securing Brackets to Teeth
Without a reliable adhesive, braces would not stay attached to the teeth.
Bonding Adhesive: A light-cured composite resin used to fix the brackets to the teeth.
This dental-grade composite resin ensures:
- Strong attachment
- Safe removal after treatment
- Minimal damage to tooth enamel
Modern bonding agents are biocompatible and highly durable.
Molar Bands: Added Stability
For additional support, especially on back teeth, orthodontists may use molar bands.
Molar Bands: Metal rings cemented around the back molars for extra stability.
These bands provide a strong base for anchoring heavy orthodontic forces.
Buccal Tubes: Supporting the Archwire
Buccal tubes are small metal attachments fixed to molar bands.
Buccal Tubes: Small metal tubes on the molar bands to secure the ends of the archwire.
They ensure that the archwire remains securely positioned throughout the treatment process.
Elastic Bands (Elastics): Correcting Bite Alignment
In many cases, orthodontists prescribe rubber bands to correct bite issues.
Elastic Bands (Elastics): Rubber bands used to correct bite alignment (overbite/underbite).
These elastics connect the upper and lower braces to adjust jaw positioning effectively.
Orthodontic Wax: Comfort and Protection
Braces can sometimes cause minor irritation to cheeks and gums.
Orthodontic Wax: Used to cover brackets that may cause irritation to the gums or cheeks.
Patients apply wax over sharp edges to prevent discomfort during the adjustment period.
Common Material Types Used in Orthodontic Braces
Orthodontic braces rely on advanced materials to ensure durability, hygiene, and effective tooth movement.
Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel: Commonly used for brackets, bands, and wires due to strength and affordability.
Benefits:
- Corrosion-resistant
- Strong and long-lasting
- Budget-friendly
Ceramic (Aluminum Oxide)
Ceramic (Aluminum Oxide): Used for aesthetic, tooth-colored brackets.
Benefits:
- Less visible
- Stain-resistant
- Popular among adults
Nickel-Titanium (NiTi)
Nickel-Titanium (NiTi): Frequently used for flexible, shape-memory archwires.
Benefits:
- Flexible
- Applies gentle continuous pressure
- Ideal for early treatment stages
Cobalt-Chromium
Cobalt-Chromium: High-strength, corrosion-resistant material for specialized brackets.
Used in complex orthodontic cases requiring additional strength.
Optional and Maintenance Materials for Braces
Proper maintenance is crucial for successful orthodontic treatment.
Cleaning Tools
- Floss Threaders: For cleaning under wires.
- Interdental Brushes: For cleaning between brackets.
These tools help prevent plaque buildup and maintain oral hygiene.
Pain Relief Solutions
- Over-the-counter medications for discomfort
- Saltwater rinses
- Cold compresses
These solutions help manage temporary soreness after adjustments.
Why Material Quality Matters in Orthodontic Treatment
The quality of materials directly affects:
- Treatment duration
- Patient comfort
- Risk of breakage
- Final alignment results
Clinics in Abu Dhabi use internationally approved orthodontic materials to ensure patient safety and effective treatment outcomes.
Modern Innovations in Orthodontic Materials
Orthodontics has evolved significantly. Today’s materials are:
- More biocompatible
- More durable
- Less noticeable
- More comfortable
Advanced ceramic brackets and memory archwires make treatment faster and more discreet than ever before.
Choosing the Right Orthodontic Braces in Abu Dhabi
When considering orthodontic treatment in Abu Dhabi, it’s important to consult a qualified orthodontist who can recommend the right materials based on:
- Severity of misalignment
- Budget
- Aesthetic preferences
- Treatment timeline
Each material serves a unique purpose, and the correct combination ensures optimal results.
Final Thoughts
Orthodontic braces are carefully engineered systems made from high-quality materials designed to straighten teeth safely and effectively. From stainless steel brackets to nickel-titanium archwires, elastic ligatures, bonding adhesives, molar bands, and buccal tubes—each component plays a crucial role in transforming smiles.
Orthodontic braces consist of several key materials designed to straighten teeth, primarily including metal or ceramic brackets, archwires (stainless steel or nickel-titanium), elastic ligatures, adhesive bonding resin, molar bands, and buccal tubes. These components work together to apply consistent pressure, with optional accessories like wax for comfort.
Understanding what materials are needed for orthodontic braces helps patients feel more confident about their treatment journey—especially when seeking high-quality orthodontic care in Abu Dhabi.
If you’re considering braces, consult a trusted orthodontic specialist in Abu Dhabi today to determine the best materials and treatment plan for your smile transformation.